What is Keratoconus?

Photo by Pixabay
Keratoconus is a progressive eye disorder that affects the cornea, the clear, dome-shaped front surface of the eye. In this condition, the cornea gradually thins and resembles a more cone-like shape, leading to visual distortion and impairment.
Signs and Symptoms
Early signs of keratoconus may include blurred or distorted vision, increased sensitivity to light, and changes in prescription eyeglasses or contact lenses. As the condition progresses, patients may experience worsening vision, increased astigmatism, and even scarring of the cornea.
Causes and Risk Factors
While the exact cause of keratoconus is unknown, certain factors may contribute to its development. These include genetic predisposition, environmental factors such as excessive eye rubbing, and certain systemic conditions.
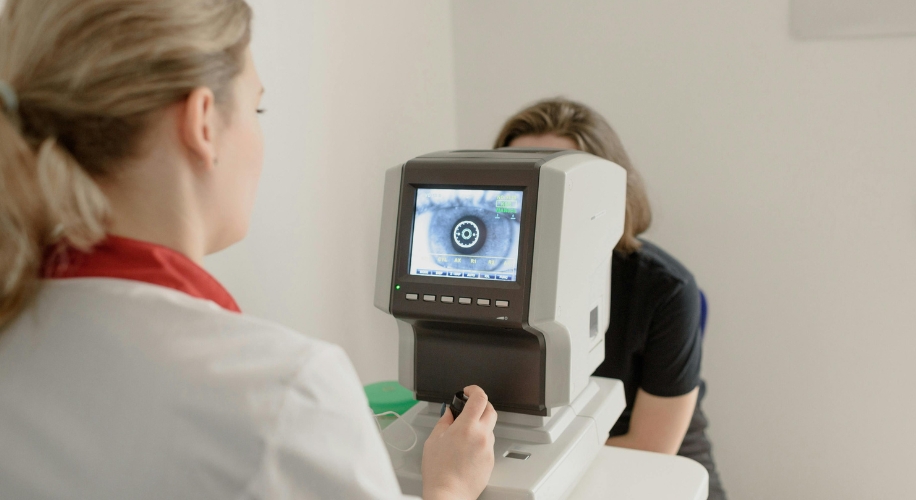
Diagnosis
Diagnosing keratoconus typically involves a comprehensive eye examination, including tests such as corneal topography to map the shape of the cornea, and corneal pachymetry to measure its thickness. Additionally, doctors may perform a slit-lamp examination to evaluate the corneal structure and look for characteristic signs of keratoconus.
Photo by Ksenia Chernaya
Treatment Options
Treatment for keratoconus aims to improve vision and halt the progression of the condition. Options may include:
- Glasses or Contact Lenses: Initially, mild cases of keratoconus may be managed with prescription glasses or soft contact lenses. Specialized contact lenses, such as rigid gas permeable (RGP) lenses or scleral lenses, may be prescribed for more advanced cases to provide better visual acuity and corneal support.
- Corneal Crosslinking: This minimally invasive procedure involves applying riboflavin (vitamin B2) eye drops to the cornea, followed by exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light. Corneal crosslinking strengthens the corneal collagen fibers, helping to stabilize and strengthen the cornea to slow or halt the progression of keratoconus.
- Intacs: Intacs are small, semi-circular plastic inserts that are surgically placed within the cornea to flatten and reshape its curvature. This can improve visual acuity and reduce the irregular astigmatism associated with keratoconus.
- Corneal Transplant: In severe cases where other treatments are ineffective, a corneal transplant (keratoplasty) may be necessary. During this procedure, the irregular corneal tissue is removed and replaced with healthy donor tissue.
Photo by Pixabay
Patients with Keratoconus
Keratoconus is a complex eye condition that requires early diagnosis and appropriate management to maintain vision and quality of life. Regular monitoring by an eye care professional is important to assess vision changes and the progression of the condition. Patients should also avoid rubbing their eyes excessively, as this can exacerbate corneal thinning and bulging. Nowadays, advances in treatment options and ongoing research allow individuals with keratoconus to manage their condition and maintain optimal eye health.




 Canada
Canada